Weathering new challenges
The European economy is now entering its fourth year of recovery and growth continues at a moderate rate, driven mainly by consumption. At the same time, much of the world economy is grappling with major challenges and risks to European growth are therefore increasing.
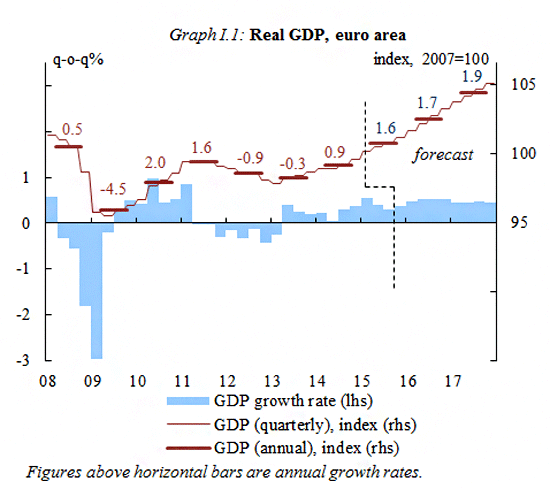
A broad-based recovery across Member States
In 2015, economic output either increased or was stable in every Member State. By 2017, the economies of all Member States are expected to be expanding. GDP growth rates will, however, continue to differ substantially due to both structural features and different cyclical positions.
Private consumption is expected to remain the main driver of growth this year and next, supported by an improving labour market and growing real disposable incomes. Investment should also gradually benefit from increasing demand, improved profit margins, favourable financing conditions and gradually lower pressure to deleverage.
 |
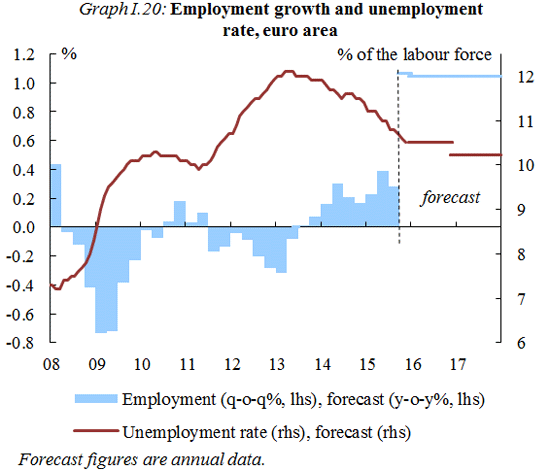
Labour market conditions continue to improve
Employment should continue to rise modestly. Unemployment rates are set to continue falling, albeit at a slower pace than last year. The decline should be more pronounced in Member States where labour market reforms have been implemented. The unemployment rate in the euro area is expected to fall from 11% in 2015 to 10.5% in 2016 and 10.2% in 2017. In the EU unemployment should fall from 9.5% in 2015 to 9.0% this year and 8.7% next.
 |
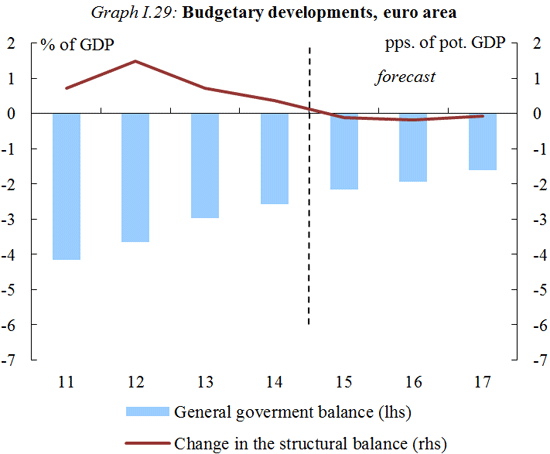
More supportive fiscal stance; deficits decline further
The aggregate general government deficit in the euro area is expected to decline further thanks to stronger economic activity and, to a lesser extent, lower interest expenditure.
In the euro area, the general government deficit is expected to have fallen to 2.2% of GDP in 2015 (EU 2.5%) and should fall further to 1.9% of GDP this year (EU 2.2%) and 1.6% of GDP in 2017 (EU 1.8%). The fiscal stance of the euro area is expected to become slightly more supportive to the economic recovery this year. In the EU, it is set to remain broadly neutral. The debt-to-GDP ratio of the euro area is forecast to decline from its peak of 94.5% in 2014 (EU 88.6%) to 91.3% in 2017 (EU 85.7%).
 |
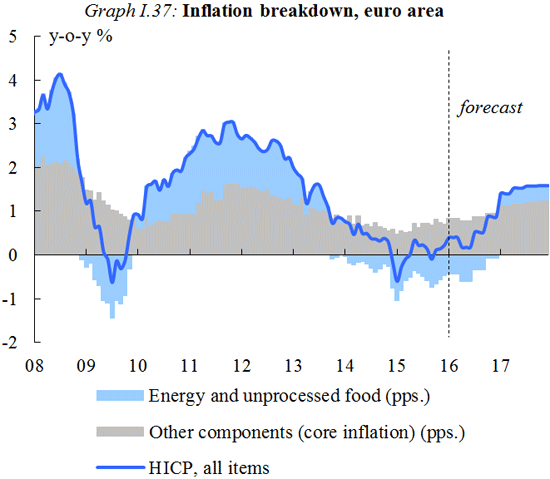
Further decline in oil prices temporarily drives down inflation
Annual inflation in the euro area was only slightly above zero towards the end of 2015, mainly due to a further drop in oil prices. Consumer prices in the euro area are expected to remain very low in the first half of the year and should start picking up in the second half when the impact from the sharp fall in oil prices abates. For 2016 as a whole, euro area annual inflation is now forecast at only 0.5%, partly because wage growth remains subdued. Inflation is expected to pick up gradually and to reach 1.5% in 2017 as higher wages, higher domestic demand and a moderate pick-up in oil prices increase price pressures.
 |
Exports resilient to further slowdown in global growth
Given the deterioration of the global economic outlook, the recovery of the global economy (excluding the EU) is now forecast to be slower than expected in the autumn. In fact global growth in 2015 is set to have been at its weakest since 2009. Euro area export growth should accelerate over the course of 2016 following a moderation in the second half of 2015. This is due to lagging effects from the euro’s past depreciation, lower unit labour costs, and a gradual increase in foreign demand.
Outlook is subject to increased risks
The economic outlook remains highly uncertain and overall risks are increasing. These include lower growth in emerging markets, a disorderly adjustment in China, and the possibility that further interest rate rises in the United States could cause disruption in financial markets or hurt vulnerable emerging economies and weigh on the outlook. A further fall in oil prices could also have a negative effect on oil-exporting countries and lower demand for EU exports. Risks from within the EU could also have an impact on confidence and investment. On the other hand, the combination of current supportive factors could translate into greater momentum than anticipated, especially if investment were to rebound.
Background
This forecast takes into consideration all relevant available data and factors, including assumptions about government policies, up until and including 22 January 2016. Only policies credibly announced and specified in adequate detail are incorporated. Projections assume no policy changes. This forecast is also based on a set of external assumptions concerning exchange rates, interest rates and commodity prices. The numbers used reflect market expectations derived from derivatives markets at the time of the forecast.
The Commission is due to update its economic forecast in May 2016.
Economic forecast documents
- 12 JANUARY 2017
- 17 JANUARY 2017
- 17 JANUARY 2017
Economic forecast thematic boxes
- 17 JANUARY 2017
- 17 JANUARY 2017
- 17 JANUARY 2017
- 17 JANUARY 2017
- 17 JANUARY 2017
Media
- Winter Economic Forecast 2016 infographic
- EC press conference Commissioner Pierre MOSCOVICI
- Press conference Q & A
- Forecast presentation
- Press release IP/16/214
Related documents
- Data source: Annual macroeconomic database (AMECO)
